Thin wall molding is a specialized injection molding process used to manufacture plastic parts with relatively thin wall sections while maintaining structural integrity, dimensional stability, and consistent quality. It is widely applied in industries where high-volume production, material efficiency, and precise tolerances are required.
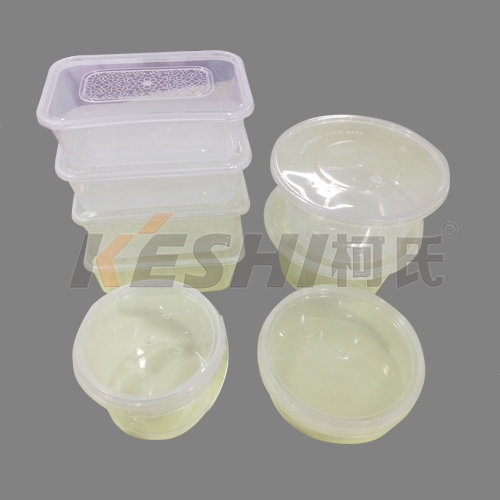

What Is Thin Wall Molding?
Thin wall molding refers to the injection molding of plastic parts with wall thicknesses that are significantly thinner than those produced using conventional molding processes. In many applications, wall thicknesses range from approximately 0.3 mm to 1.0 mm, depending on the material and part geometry.
This process relies on:
- High-speed injection molding machines
- Optimized mold designs with efficient flow paths
- Specialized materials with good flow characteristics
Thin wall molding is commonly used for:
- Food and beverage containers
- Packaging lids and caps
- Medical disposables
- Consumer product housings
Why Is Thin Wall Molding Important?
Material Efficiency and Cost Control
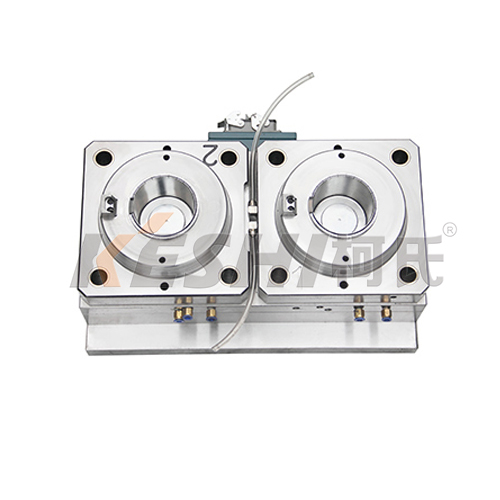

Thin wall molding reduces the amount of plastic used per part. Over large production volumes, this can result in meaningful material cost savings and lower overall product weight.
High-Volume Production Efficiency
Because thin wall parts cool quickly, cycle times are shorter compared to conventional molding. This enables:
- Higher output per machine
- Lower energy consumption per part
- Improved production planning
Support for Lightweight Design
Many industries aim to reduce packaging weight for transportation and handling efficiency. Thin wall molding supports lightweight designs without compromising basic strength requirements.
Consistent Quality at Scale
With properly designed molds and controlled processes, thin wall molding can deliver:
- Uniform wall thickness
- Stable dimensions
- Repeatable performance across large batches
This consistency is critical for automated filling, sealing, and assembly systems.
Why is Thin Wall Molding Used in Manufacturing?
- Cost Efficiency: One of the primary reasons thin wall molding is used is its ability to reduce material consumption. By producing parts with thinner walls, less plastic is used, which translates to lower material costs for manufacturers. In addition, thinner parts are often lighter, which can also reduce shipping costs, especially in industries such as automotive or packaging.
- Faster Production Cycle Times: Thin wall molding enables faster cooling times because less plastic material is involved. The shorter cooling times result in quicker cycle times, thus increasing the overall production efficiency. Manufacturers can produce a higher number of parts in a given time frame, which is particularly important in industries that require large volumes of plastic components.
- Improved Product Performance: Thin wall molding allows manufacturers to design lightweight products without compromising on strength or durability. When done correctly, thin-walled parts can be just as strong as thicker components, providing both performance and cost benefits.
What is Thin Wall Injection Molding and How Does it Differ from Traditional Injection Molding?
Thin wall injection molding is a variation of the traditional injection molding process where parts are produced with walls that are thinner than 1 millimeter, in some cases as thin as 0.2 millimeters. The process requires the use of high precision and specialized equipment due to the challenges posed by the thin walls.
What Challenges Are Associated with Thin Wall Injection Molding?
- Material Flow and Distribution: One of the key challenges of thin wall injection molding is ensuring that the plastic material flows evenly throughout the mold cavity. The thin walls require careful control of injection speed and pressure, as the material must be injected quickly to prevent premature solidification and voids in the part. Manufacturers must also ensure that the plastic flows uniformly to avoid weak spots or defects in the final product.
- Heat Management: Thin-walled molds require efficient heat control because the material cools down much faster than thicker components. Managing the cooling process is critical to prevent warping or deformation, which can occur if the mold cools too quickly or unevenly. Specialized mold designs and advanced cooling systems are necessary to ensure uniform cooling rates.
- Material Selection: Thin wall injection molding demands the use of specific materials that have good flow characteristics and can withstand the pressures of the injection process without cracking or becoming brittle. Materials such as polycarbonate, ABS, and polypropylene are often used for thin-walled components because they maintain their strength while being lightweight.
What is Ultra Thin Wall Injection Molding and How is it Different from Regular Thin Wall Injection Molding?
Ultra thin wall injection molding is an advanced form of thin wall molding, where parts have walls that are thinner than 0.5 millimeters, and in some cases as thin as 0.1 millimeters. This technique is often used in applications where weight reduction is required or where complex designs with intricate details need to be produced. Ultra thin wall injection molding is commonly used in industries like consumer electronics, medical devices, and packaging, where space constraints and lightweight materials are crucial.
What Are the Key Challenges in Ultra Thin Wall Injection Molding?
- Precision and Control: Ultra thin wall injection molding requires the higher level of precision in both the injection molding process and the design of the molds. The thinner the wall, the more difficult it becomes to control the flow of material and the uniformity of the wall thickness. Molds need to be designed with tight tolerances to ensure consistency and avoid defects such as sink marks or short shots.
- Advanced Mold Design: Molds used for ultra thin wall injection molding are more complex and expensive to manufacture. They must be designed with highly sophisticated cooling channels to allow for uniform cooling and prevent issues such as warping or residual stress. Additionally, molds must be able to withstand higher pressures and more aggressive injection speeds due to the reduced thickness of the material.
- Material Performance and Selection: At ultra-thin thicknesses, material performance becomes even more critical. Plastics used in ultra-thin wall molding must possess exceptional flow properties and strength while being lightweight. Materials such as high-flow polycarbonate and certain grades of polypropylene are commonly used, but the choice of material will depend on the specific requirements of the application. These materials must also perform well in demanding conditions without cracking or losing their shape.
Thin wall, thin wall injection, and ultra-thin wall injection molding are specialized techniques that provide manufacturers with the ability to produce lightweight, cost-effective, and high-performance components. While they share some common features, such as the need for precision and efficient molding processes, each type of molding presents unique challenges that require specialized materials, equipment, and design considerations. Understanding the differences between these processes and their applications is key to selecting the right method for producing parts that meet the necessary performance standards.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体