How does the Chemical and Impact Resistance of Paint Bucket Molds Affect Their Performance?
In the production of paint buckets, the material properties and resistance characteristics of the molds used for manufacturing play a crucial role in determining the quality and functionality of the final product. These molds are specifically designed to endure harsh conditions and ensure the paint bucket maintains its integrity over time.
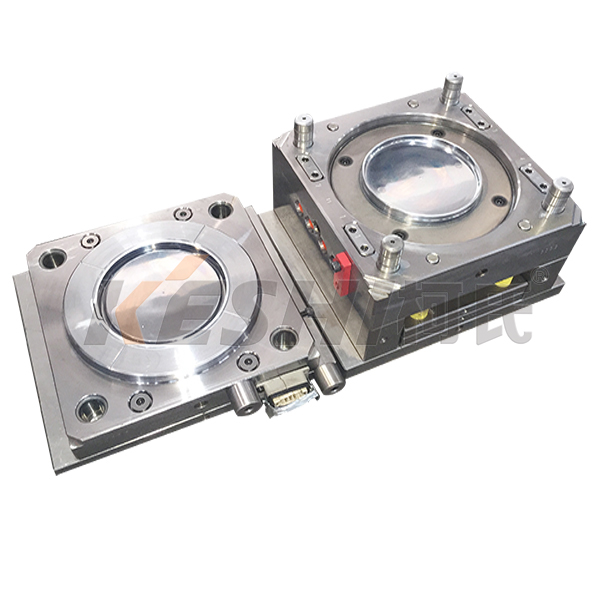

How is the Chemical Resistance of Paint Bucket Molds?
Material Selection for Chemical Resistance
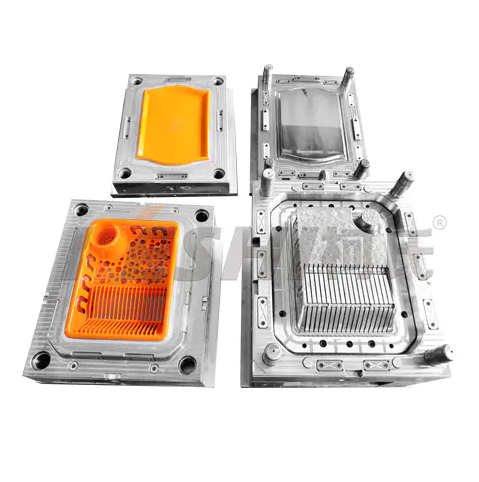
The choice of material used in paint bucket molds directly influences their chemical resistance. Materials like high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene (PP) are commonly used due to their inherent resistance to various chemicals such as acids, bases, and solvents. These materials are able to withstand exposure to different chemicals without degrading, ensuring that the paint bucket remains functional and safe for storage and transportation of paints and other substances.
Impact of Paint Solvents on Mold Materials
Paints often contain solvents and chemicals that could degrade the material of the mold. The resistance of the mold material to these substances determines how well it can maintain its integrity. For example, molds made from UV-resistant polymers ensure the bucket can endure exposure to sunlight without weakening or losing its shape, especially if the paint inside is prone to solvent evaporation.
Heat Resistance and Its Role in Chemical Resistance
The temperature at which the mold is used also plays a role in chemical resistance. During the molding process, elevated temperatures may expose the material to thermal degradation. To mitigate this, certain polymers are selected for their high melting points, which allows them to perform under the high temperatures encountered in plastic injection molding processes without losing their chemical resistance properties.
Surface Treatment for Enhanced Resistance
In addition to choosing the right materials, surface treatments like coating or adding chemical-resistant layers to the mold can further enhance the chemical resistance. These treatments help to protect the mold from becoming affected by the paint or other chemicals stored in the buckets.
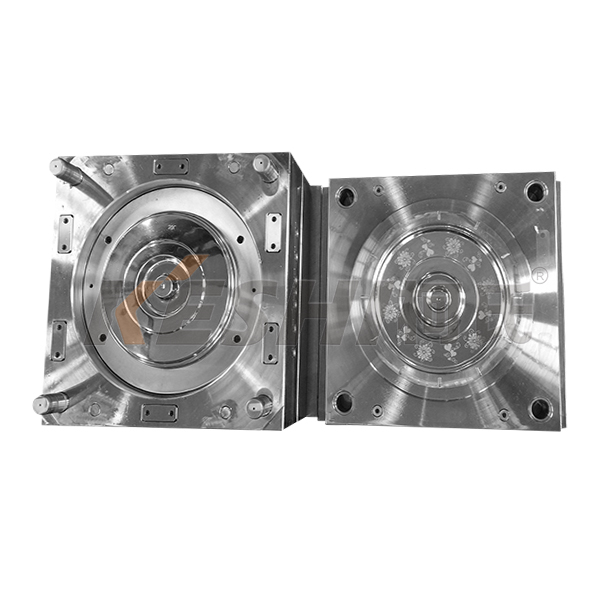

How is the Impact Resistance of Bucket Molds?
Structural Integrity and Durability
Impact resistance refers to the mold’s ability to withstand sudden external forces without breaking or deforming. Paint buckets are often exposed to rough handling, dropping, or stacking during transportation and storage. Therefore, the mold material must be strong enough to endure these impacts without affecting the structural integrity of the bucket. This is typically achieved by using materials such as reinforced polypropylene or polyethylene, which have high tensile strength.
Impact Resistance in Varying Temperatures
Molds used in the production of paint buckets must also retain their impact resistance across a range of temperatures. The resistance of the material to impact can change depending on whether it is cold or hot. Molds used for paint buckets must be designed to maintain their strength and toughness even in low-temperature environments, where materials might become brittle and prone to cracking. This is particularly important when the paint buckets are stored in outdoor environments that experience fluctuating temperatures.
Effect of Material Stiffness on Impact Resistance
Materials with higher stiffness are generally more resistant to impact, but this can come at the cost of brittleness. To achieve a good balance, certain polymers are blended to enhance their ability to absorb shock and distribute impact forces more evenly, thereby reducing the chances of damage. The use of impact modifiers in the formulation of the mold material is a common method for improving impact resistance while maintaining flexibility.
Special Considerations in the Manufacturing Process
The impact resistance of a bucket mold is also influenced by the injection molding process. Factors such as cooling time, injection speed, and pressure during the molding process play a significant role in the distribution of material within the mold. Proper molding techniques ensure that the final product has a uniform thickness and structure, contributing to better impact resistance.
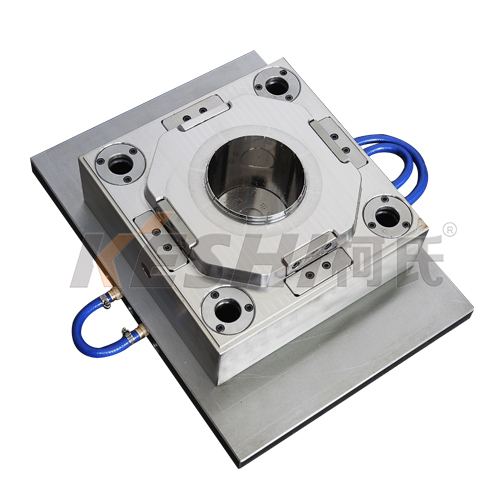

What are the Chemical Properties of Plastic Injection Molding Die?
Plastic injection molding is a highly precise process used in manufacturing various plastic products, including paint buckets, automotive parts, medical devices, and more. The die used in this process is a key component that shapes the plastic material into the desired form. The chemical properties of plastic injection molding dies are essential in determining their performance, durability, and the quality of the final product.
Corrosion Resistance of Molding Dies
One of the important chemical properties of injection molding dies is their resistance to corrosion. Molds are often exposed to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals during the injection process. Corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or special alloys, are typically used to manufacture these dies. Corrosion can bring about the degradation of the die surface, affecting the quality of the molded products and the lifespan of the mold. Therefore, corrosion resistance is essential for ensuring longevity and reliability in the manufacturing process.
Wear Resistance
Molds for plastic injection molding undergo repeated cycles of heating, cooling, and contact with molten plastic. Over time, this can cause wear on the die surfaces, bring about dimensional inaccuracies in the molded parts. The wear resistance of the mold is critical for maintaining consistent product quality. Materials used for molds are often selected for their hardness and ability to resist abrasion from the movement of molten plastic.
Thermal Conductivity and Stability
The die material must also have favorable thermal properties. It should be able to conduct heat effectively to ensure the proper cooling of the molten plastic, allowing it to solidify and retain its shape. At the same time, the material should be stable enough to withstand the constant temperature fluctuations during the molding process. If the die material has poor thermal stability, it may warp or degrade over time, negatively affecting the mold's performance.
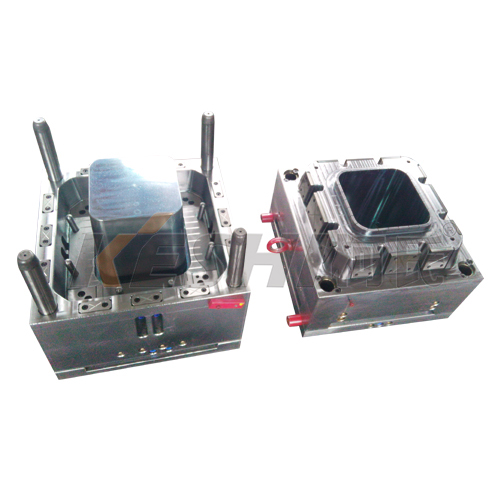

Chemical Resistance to Plastics
Plastic injection molding dies are frequently exposed to a range of polymers, some of which can be chemically aggressive or prone to leaving residues that can damage the mold. The chemical properties of the die material determine how well it can withstand these plastics without corroding or reacting negatively. High-quality injection molds are made from materials that resist chemical attacks from various plastics, including those with additives, pigments, or other reactive chemicals.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体