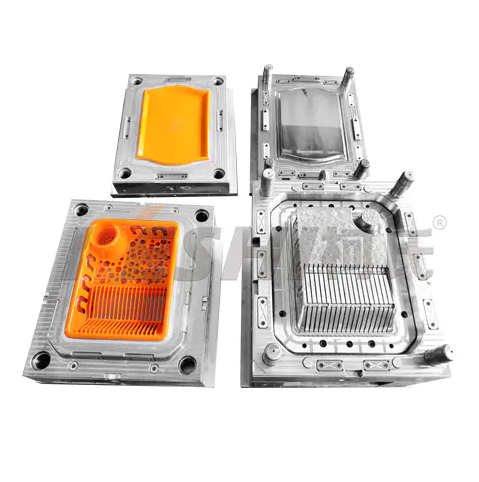
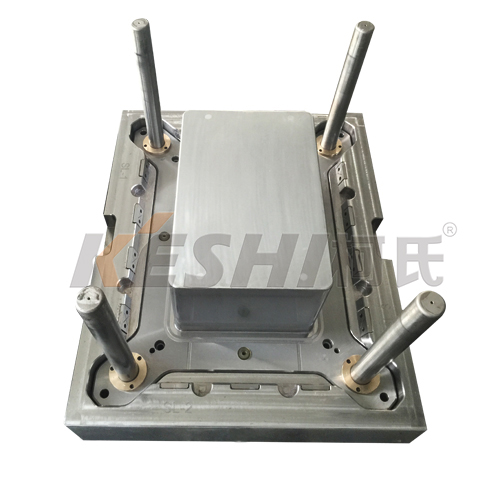
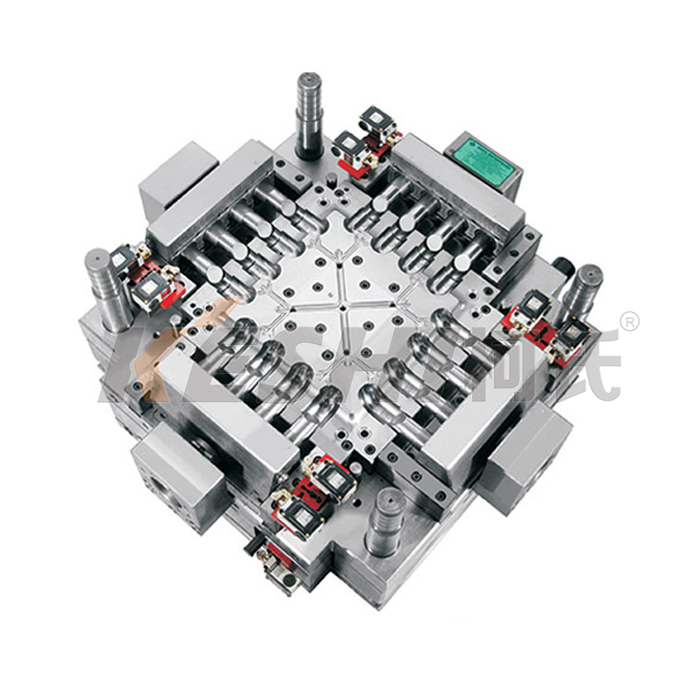
A plastic pallet mold is a precision-engineered steel mold installed in an injection molding machine. Molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity, cooled, and ejected to form a finished pallet. Compared with wooden pallets, plastic pallets produced by molds offer higher consistency, longer service life, and better suitability for automated logistics systems.
Plastic pallet molds are typically large, heavy molds due to the size and structural requirements of pallets.
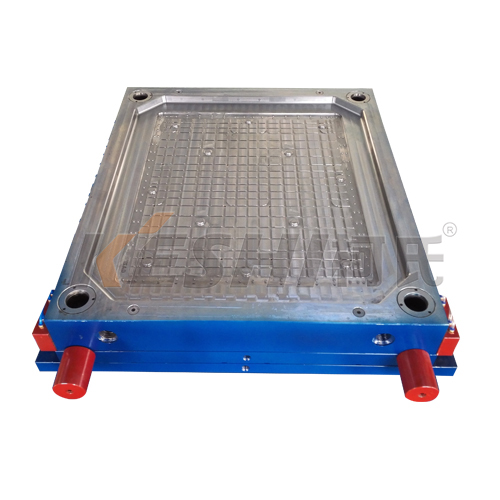

Common Types of Plastic Pallet Molds
Plastic pallet molds are classified based on pallet structure and usage requirements:
Flat top pallet mold
Smooth deck surface
Suitable for boxed or bagged goods
Grid deck pallet mold
Open structure with reinforcement ribs
Reduced material usage and faster cooling
Stackable pallet mold
Designed for stable stacking when loaded
Nestable pallet mold
Space-saving when empty
Rackable pallet mold
Designed for use in pallet racking systems
Materials Used
Plastic materials
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
Good impact resistance
Suitable for heavy-duty pallets
PP (Polypropylene)
Lower density
Often used for lighter logistics pallets
Mold steel
- P20 / 718 / 718H: Common for medium to high production volumes
- H13: Used for long service life and higher performance requirements
Manufacturing and Production Considerations
- Cycle time: Typically 60–180 seconds, depending on pallet size and thickness
- Wall thickness control: Essential for load performance
- Cooling balance: Prevents deformation and uneven shrinkage
- Automation: Often combined with robotic pallet removal
How does a Flat Top Plastic Pallet Mold differ from other types of pallet molds?
A flat top plastic pallet mold produces pallets with a smooth, continuous deck surface. This design is common in industries that require stability for stacked goods, easier cleaning, and compatibility with automated systems. The key differences between flat top pallet molds and other pallet mold types lie in structure, function, and manufacturing requirements.
Structural differences
Deck surface
Flat top pallets have a uniform, uninterrupted surface.
Other types, such as grid deck or open deck pallets, have openings and ribbed patterns for weight reduction.
Reinforcement design
Flat top pallets often require internal reinforcement to maintain strength without visible grid structures.
Open deck pallets rely on visible ribs and grid frameworks for stability.
Edge design
Flat top pallets typically have straight edges and smooth sides.
Other pallet types may include chamfered corners, reinforced edges, or special entry points for forklifts.
Functional differences
Application suitability
Flat top pallets are used where goods need a stable surface, such as electronics, furniture, or packaged consumer goods.
Grid or open deck pallets are more common in heavy industry or agriculture where drainage and airflow are needed.
Cleanliness and hygiene
Flat top pallets are easier to clean, making them suitable for food, pharmaceuticals, and medical supplies.
Open deck pallets can trap debris and require more effort to clean.
Compatibility with automated systems
Flat top pallets are preferred in automated warehouses due to predictable surface contact and fewer irregularities.
Other pallet types may create issues with automated stacking or conveyor systems.
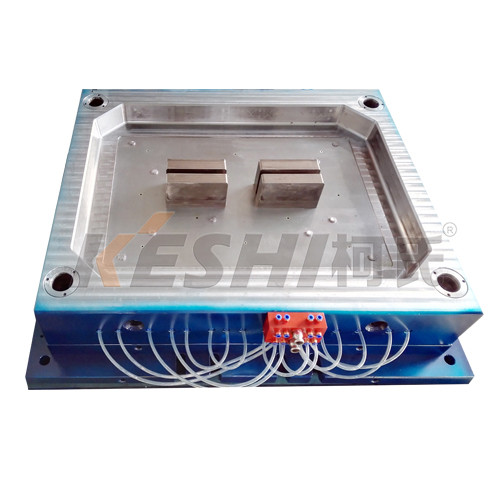

Manufacturing differences
Mold complexity
Flat top pallet molds need precise cavity design to ensure uniform thickness and strength.
Open deck molds may be less complex but require careful rib alignment.
Cooling and cycle time
Flat top molds often have longer cooling times due to larger solid surface areas.
Open deck molds cool faster because of reduced mass and more surface area exposure.
Can the size and shape of a Plastic Pallet Mold be customized?
The size and shape of plastic pallet molds can be customized based on the specific needs of the end user. Customization is one of the main advantages of plastic pallets compared to standard wooden pallets, as it allows manufacturers to design pallets that fit unique storage systems, product dimensions, and handling methods.
Common customization options
Dimensions
Length, width, and height can be adjusted to match storage racks or shipping requirements.
Common sizes include 1200×1000 mm or 1200×800 mm, but custom sizes are feasible.
Deck type and pattern
Flat top, grid top, or mixed deck designs can be chosen based on product stability and airflow needs.
Weight capacity
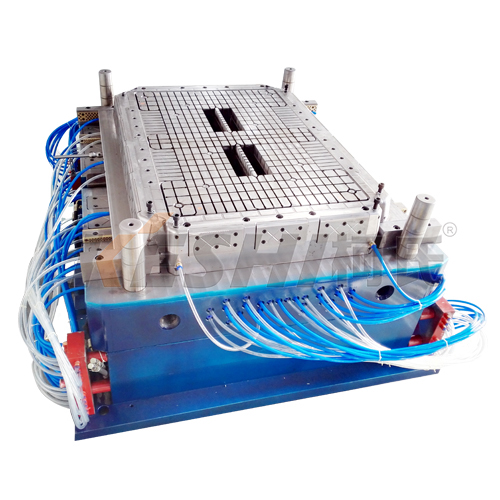
Mold design can be modified to increase or decrease load capacity by changing rib thickness and internal structure.
Forklift entry design
Four-way or two-way entry can be customized to match handling equipment.
Color and material
Mold can support different plastic materials and colors based on branding or functional requirements.
Design considerations
Load and stacking requirements
The intended load determines the reinforcement structure within the mold.
Storage conditions
If pallets will be used in cold storage, the mold design may include thicker walls for added strength.
Compatibility with automated systems
Pallet dimensions must align with conveyor belts, automated guided vehicles, and racking systems.
Customization process
Consultation and specification
Manufacturers typically begin with a detailed needs assessment, including load, handling, and storage environment.
CAD design and simulation
The mold is designed in CAD software, often with structural simulation to verify strength.
Prototype and testing
A sample pallet is produced and tested before full-scale mold production.
Mold manufacturing and validation
Once approved, the mold is manufactured and validated through trial runs.
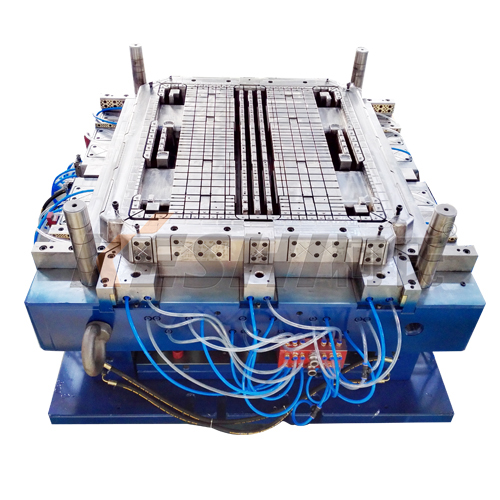
What is the weight-bearing capacity of a Plastic Mold for Pallets?
The weight-bearing capacity of a plastic pallet depends on both the pallet design and the mold structure. Mold design directly influences load capacity by determining the internal rib structure, wall thickness, and overall stability of the finished pallet. While specific capacity varies widely, plastic pallets generally offer predictable performance under controlled conditions.
Factors affecting load capacity
Material type
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene (PP) are common.
Material properties influence rigidity, impact resistance, and deformation.
Deck structure
Flat top pallets typically require stronger internal reinforcement to support loads evenly.
Grid or open deck pallets may concentrate strength in ribs.
Rib and wall thickness
Thicker ribs and walls increase load capacity but also increase weight and cost.
Design type
One-piece molded pallets generally offer higher strength and stability.
Two-piece or assembled pallets may have different load characteristics.
Typical load capacities
Static load capacity
Refers to weight supported when the pallet is stationary.
Many plastic pallets support between 1,000 kg and 3,000 kg statically, depending on design.
Dynamic load capacity
Refers to weight supported during movement by forklift or pallet jack.
Typical dynamic capacities range from 500 kg to 1,500 kg.
Racking load capacity
Refers to weight supported when pallet is placed in a racking system.
Racking capacity depends heavily on pallet stiffness and rack support points.
Design implications for molds
Reinforcement placement
Mold design must ensure reinforcement aligns with load-bearing zones.
Uniform wall thickness
Consistent thickness prevents weak points and deformation under load.
Cooling and shrinkage control
Proper cooling channels in the mold reduce warping and ensure dimensional accuracy.
Testing and validation
Load testing
Pallets are tested under static, dynamic, and racking conditions to confirm capacity.
Simulation
Finite element analysis (FEA) is often used during design to predict performance.
Standards compliance
Many manufacturers test according to industry standards to ensure reliability.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体