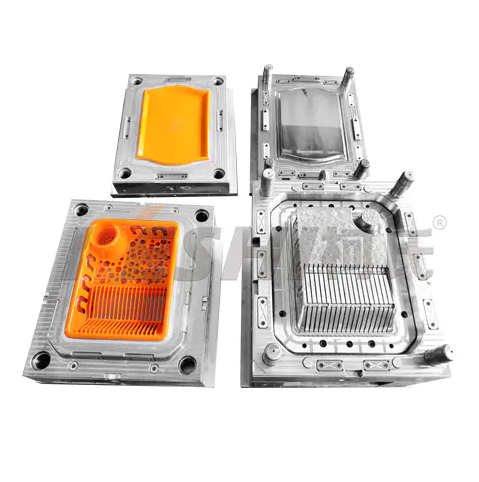
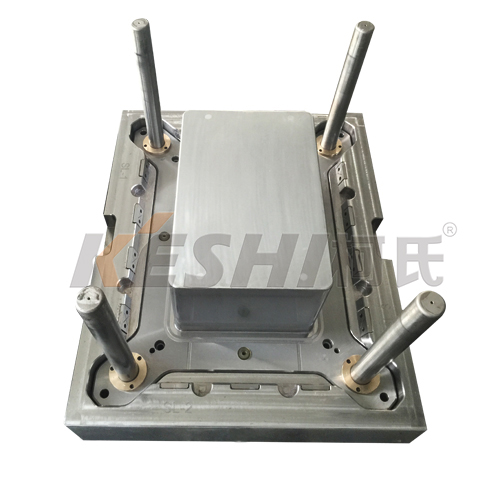
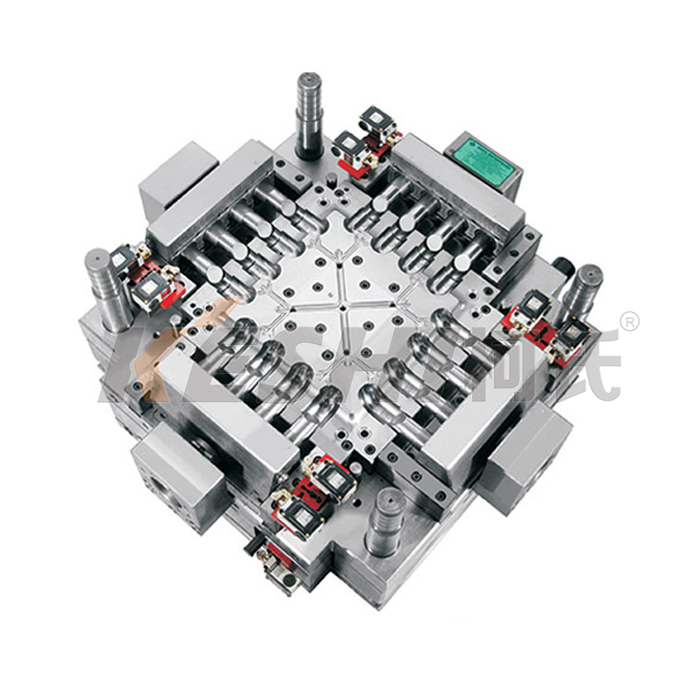
A logistics containers injection mould is a precision tool used in injection molding machines to manufacture plastic containers for storage, transportation, and material handling. These containers are widely used in logistics, warehousing, manufacturing, retail distribution, and automated handling systems, where consistency, durability, and dimensional accuracy are required.
Logistics containers injection moulds are designed to produce standardized plastic boxes, crates, totes, or bins in high volumes. Molten plastic is injected into the mould cavity, cooled under controlled conditions, and ejected as a finished container. The mould determines the container’s size, shape, wall thickness, stacking structure, and functional features.

Compared with alternative forming methods, injection moulding offers better repeatability and surface quality, which is important for logistics containers used in automated systems.
Common Types of Logistics Container Moulds
Solid wall container moulds
Used for closed boxes requiring protection from dust or moisture.
Ventilated container moulds
Designed with holes or slots for airflow, commonly used in food logistics.
Stackable container moulds
Provide stable stacking when loaded.
Nestable container moulds
Reduce storage space when empty.
Foldable container moulds
Incorporate moving components and higher mould complexity.
Advantages of Injection Moulded Logistics Containers
- Consistent dimensions
- High production efficiency
- Reusability and durability
- Compatibility with automation
- Lower cost per unit at scale
Logistics Containers Injection Mould: What are the cost and potential economic benefits of investing in logistics box molds?
Investing in logistics box molds involves a balance between upfront costs and long-term economic benefits. The decision typically hinges on the expected production volume, the required durability of the boxes, and the efficiency gains in the supply chain. Injection molds for logistics containers are a significant capital investment, but they can also bring about measurable savings over time if the design and production plan align with business needs.
Cost components of logistics box molds
Mold design and engineering
Includes CAD design, structural simulation, and prototype validation.
Costs vary based on complexity and required precision.
Material and manufacturing
High-quality steel, CNC machining, and heat treatment are common expenses.
Larger molds require more material and longer machining time.
Tooling and trial runs
Test shots, mold adjustments, and validation cycles add to the cost.
Maintenance and repairs
Molds require regular maintenance to maintain performance.
Over time, wear and tear may require repairs or part replacement.
Economic benefits of logistics box molds
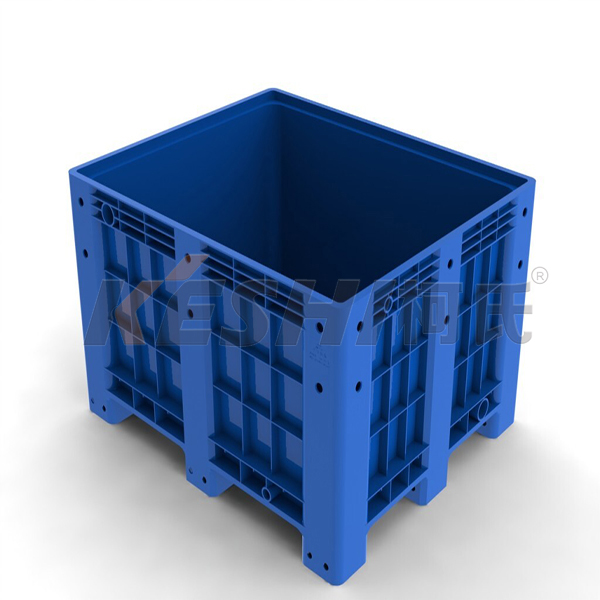

Lower unit cost at scale
Higher initial costs are offset by lower per-unit costs as volume increases.
Improved supply chain efficiency
Standardized containers simplify stacking, storage, and transportation.
Reduced product damage
Consistent quality and design reduce breakage during handling.
Reusable and durable logistics containers
Long-term use reduces the need for single-use packaging.
Cost-benefit comparison
|
Item |
Initial Cost |
Ongoing Cost |
Economic Impact |
|
Mold tooling |
High |
Low |
Enables mass production |
|
Material cost per box |
Medium |
Low |
Reduced with volume |
|
Maintenance |
Low |
Medium |
Ensures consistent output |
|
Logistics efficiency |
N/A |
Low |
Saves handling time |
|
Damage reduction |
N/A |
Low |
Reduces replacement cost |
The cost of logistics box molds is typically justified when production volumes are high and the boxes are intended for long-term use. Companies should evaluate both direct costs and indirect savings, such as reduced handling time and fewer damaged goods. When aligned with operational goals, investing in logistics box molds can support more predictable supply chain performance and lower long-term costs.
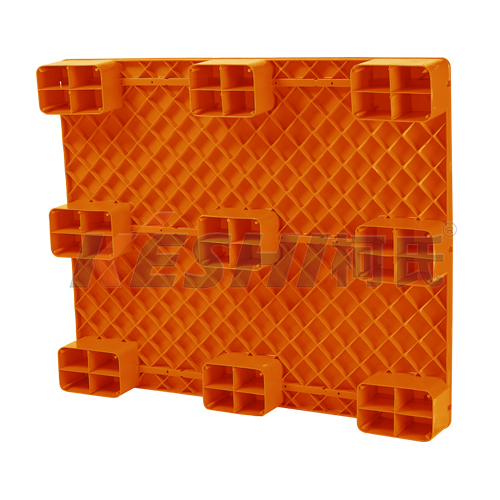
Logistics Injection Plastic Pallet Mould: What should I know?
What is a logistics injection plastic pallet mold?
A logistics injection plastic pallet mold is a steel tool used in injection molding machines to produce plastic pallets. These pallets are designed for storage and transportation and are commonly used in warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing facilities.
What are the common types of pallet molds?
- Flat top pallet molds
- Grid deck pallet molds
- Nestable pallet molds
- Stackable pallet molds
Each type is designed for different logistics requirements, such as space-saving storage or load-bearing needs.
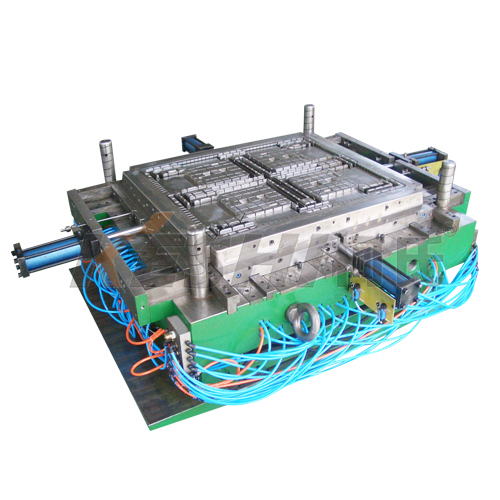
What materials are used for pallets produced by these molds?
Common materials include:
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
- PP (Polypropylene)
These materials offer a balance between strength, durability, and cost.
What are the key design considerations?
- Load capacity
- Deck type
- Forklift entry design
- Reinforcement ribs and wall thickness
- Compatibility with automated systems
How does mold quality affect pallet performance?
A high-quality mold ensures consistent dimensions, uniform wall thickness, and reliable strength. Poor mold design can bring about warping, weak points, and reduced load capacity.
What is the typical production cycle time?
Cycle time depends on pallet size, material, and mold design. It generally ranges from 30 seconds to 3 minutes per pallet. Cooling time and mold complexity are major factors.
Can the mold be customized?
Molds can be customized for size, shape, entry design, color, and load capacity based on specific logistics requirements.
What maintenance is required?
Regular maintenance includes:
- Cleaning and lubrication
- Inspection for wear
- Replacement of wear parts
- Mold polishing or repair as needed
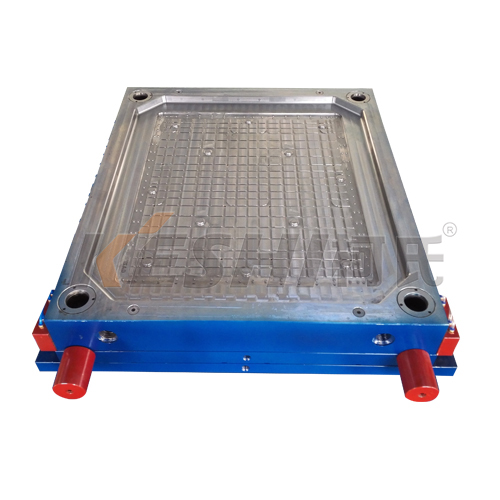
Logistics Box Molds: What are the design standards for logistics box molds?
Designing logistics box molds requires adherence to standards and specifications that ensure performance, durability, and compatibility with handling systems. Standards can vary by region and industry, but there are common guidelines that apply to logistics containers.
Structural design standards
Wall thickness and rib design
Ensure uniform wall thickness to prevent warping and weak points.
Reinforcement ribs should be designed to support expected loads.
Corner and edge strength
Corners and edges must withstand repeated stacking and impact.
Stacking and nesting requirements
Boxes should be designed for stable stacking when full and efficient nesting when empty.
Dimensional standards
Standard sizes
Many logistics boxes follow standard dimensions for compatibility with pallets, shelves, and containers.
Tolerance control
Tight tolerances are required for consistent stacking and automated handling.
Material and performance standards
Material selection
HDPE and PP are common materials, chosen for durability and resistance to impact and chemicals.
Temperature resistance
Designs should consider operating temperature ranges, especially for cold storage or outdoor use.
Load-bearing capacity
Design must meet static, dynamic, and stacking load requirements.

Safety and handling standards
Ergonomics
Handles and grip areas should be designed for user comfort and safety.
Labeling and traceability
Mold designs should include space for labeling, barcodes, or RFID tags.
Manufacturing standards
Mold flow and cooling
Proper gate design and cooling channels ensure consistent quality and reduce cycle time.
Surface finish
Smooth surfaces reduce contamination and simplify cleaning.
Compliance standards
Industry-specific regulations
Food, medical, and pharmaceutical logistics boxes may require additional standards for hygiene and safety.
Recycling and environmental standards
Design should consider material recyclability and end-of-life disposal.
Logistics box mold design should be guided by structural, dimensional, material, safety, and compliance standards. Following these specifications helps ensure the containers perform reliably in real-world logistics environments and support efficient supply chain operations.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体